Data protection overview
NuoDBaaS safeguards customer data by automating the database backup process through user-defined policies that manage backup creation and retention. These backups can be used to create new databases or restore a database’s captured state and configuration. This section describes the backup and cloning mechanisms and offers insights into the internal architecture.
Prerequisites
NuoDBaaS backup solution depends on several external components that must be provisioned in the Kubernetes cluster. It leverages Container Storage Interface (CSI) driver and external snapshotter to backup block volumes.
Note
Follow the documentation from your cloud provider to install and configure the CSI driver. For more information on Amazon Elastic Kubernetes Service (EKS) see Store Kubernetes volumes with Amazon EBS.
Compatibility
Refer to the table below for supported configurations and backup capabilities.
| Minimum NuoDB Control Plane version | Minimum NuoDB version | Minimum NuoDB Helm charts version | Capabilities |
|---|---|---|---|
| v2.4.1 | v5.1.1 | v3.8.2 | On-demand backup and clone for DBaaS databases. Snapshot-based backup using fsfreeze for databases with external journal enabled |
| v2.4.1 | v6.0.2 | v3.9.0 | Snapshot-based backup using hotsnap for databases with external journal enabled |
| v2.6.1 | v6.0.2 | v3.9.0 | Backup policies with scheduling and retention |
| v2.7.0 | v6.0.2 | v3.9.0 | Advanced backup retention configuration |
Architecture
NuoDBaaS delivers backup support in a cloud-agnostic manner by leveraging several cloud-native components deployed in the Kubernetes cluster.
CSI driver
Implements the CSI interface which provisions volumes and snapshots in the cloud provider’s storage system.
External snapshot controller
Implements the CSI interface and reconciles VolumeSnapshot and VolumeSnapshotContent resources in the Kubernetes cluster.
Communicates with a CSI driver configured in the VolumeSnapshotClass to manage snapshot lifecycle on the cloud.
Volume snapshot class
Configures the CSI driver and specifies a snapshot class that is used to execute a volume snapshot.
If there is no default VolumeSnapshotClass configured in the cluster, you must specify one using --backup-volumesnapshot-class option.
Backup manager
A backup manager is a system that backs up Kubernetes applications including their data and configuration. It is responsible for creating, executing, storing backups, and managing the catalog of available backups.
NuoDBaaS provides an embedded backup manager with the following capabilities:
- Creates
VolumeSnapshotresources to capture snapshots of selected database volumes using the cloud provider’s storage system - Uses
Secretresources to capture database configuration and manage a backup catalog of the available backups - Executes HTTP backup hooks to prepare the database for backup operation
Backup plugin
Implements the NuoDB backup interface (NBI) for the NuoDB Control Plane to communicate with the backup manager.
The DatabaseBackup custom resource models a backup taken from a specific database in NuoDBaaS.
The plugin decouples DatabaseBackup resource lifecycle (scheduling, deleting, and listing of backups) from the backup execution strategy (creating, storing, importing, and exporting backups).
NuoDBaaS provides an embedded backup plugin that communicates with the embedded backup manager.
Backup catalog
The target location where the backup configurations and metadata are stored. The backup catalog is not used for the data backup as the snapshots are stored on the cloud provider’s storage system.
Caution
The embedded backup manager uses Secret resources for a backup catalog bound to a single Kubernetes cluster.
You must have a process that backs up the Kubernetes etcd database to recover from a disaster including the loss of the Kubernetes cluster.
Backup hooks
Backup hooks are used within the NuoDB Helm charts and prepare the database for a backup. Responsible for storing metadata in the database volumes (such as backup ID) supplied later during restore.
A NuoDB database with an external journal enabled requires synchronization before taking snapshots.
Backup hooks support several synchronization strategies (supplied via the freezeMode Helm value):
hotsnap(recommended) - Uses NuoDB product support for pausing archive writes. Supported from NuoDB v6.0.2 and above.fsfreeze- Usesfsfreezebinary to suspend archive reads and writes. This mode requires a privileged sidecar container.suspend- The SM process is suspended completely and then resumed usingkill -STOPandkill -CONT. This is to enable usage in environments wherefsfreezecannot be invoked on the archive filesystem. Only for testing purposes.
NuoDBaaS will select the best synchronization strategy depending on the NuoDB product version and NuoDB Helm chart version installed.
We recommend using the latest NuoDB version and hotsnap since it has several advantages such as:
- Archive reads are not blocked so backup does not prevent cache misses from being fetched
- Support automatic archive unfreeze with configurable timeout in case performing the snapshot backup takes longer than expected
- Unintentional Storage Manager restart during backup unfreezes the archive volume
Note
To minimize the impact on SQL application clients, the backup manager unfreezes volumes immediately after the snapshot is created on the cloud provider.
Some cloud providers, like Outscale, consider a snapshot to be a consistent cut after it is reported ready by the CSI driver.
You must set --backup-post-hooks-on-snapshot-ready=true option when deploying NuoDBaaS in such environments.
For more information about Outscale Block Storage Unit (BSU) snapshots see About Snapshots.
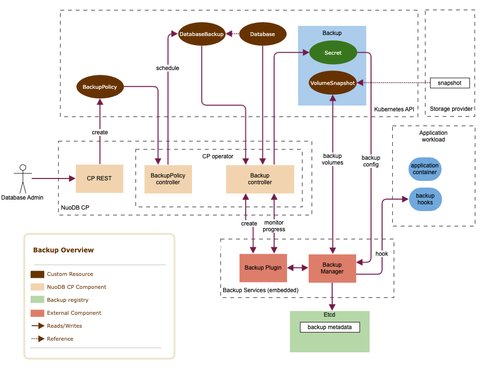
Backup flow
A BackupPolicy custom resource defines the set of rules for performing backup scheduling and retention.
A database must satisfy the set of rules for at least one backup policy to ensure backups are scheduled for it.
A DatabaseBackup custom resource defines individual database backup requests and holds information for the backup (e.g. backup ID, phase, etc.).
NuoDBaaS monitors backup policies and schedules backups by creating DatabaseBackup resources.
Deleting a BackupPolicy does not delete or invalidate database backups that it has created.
NuoDBaaS prepares the database configuration and database PVCs for backup.
The backup plugin collaborates with the backup manager to execute backup hooks, create VolumeSnapshot resources for the selected database volumes, and capture the database configuration.
NuoDBaaS monitors the backup progress and updates the DatabaseBackup resource.
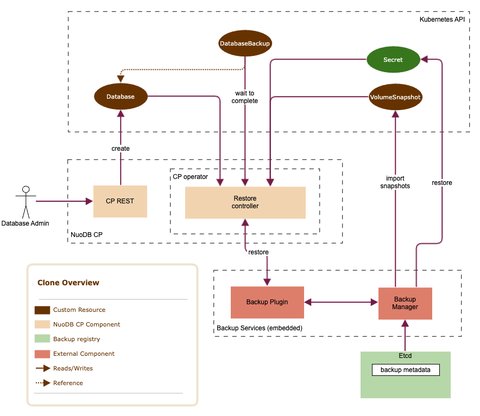
Restore (clone) flow
A Database custom resource may reference a DatabaseBackup as a restore source.
NuoDBaaS validates the backup and merges the database spec with the one stored in the configuration backup.
The backup manager imports the VolumeSnapshot and VolumeSnapshotContent resources corresponding to the backup into the cluster so that the NuoDB Helm charts can utilize them as a source for the new database volumes.
Export backup
The NuoDBaaS administrator must export a backup taken on a database from another cluster manually. After import, this backup is used to restore a database in the target cluster.
List the available backups on the source cluster.
kubectl --context source-cluster get secret -l backup.cp.nuodb.com/backup-idThe backup Secret contains metadata about the actual backup and has a name with the format of cp.nuodb.com.backup.<org>-<proj>-<db>-<name>.
Copy the secret from the source cluster to the target cluster.
kubectl --context source-cluster get secret \
cp.nuodb.com.backup.acme-messaging-demo-20241009000000 -o yaml | kubectl --context target-cluster apply -f -For more information on how to import the backup, see Import backup
Caution
NuoDBaaS does not support exporting backups from the Kubernetes cluster across regions.
Configure backup controller
Embedded backup plugin and manager are enabled by default if VolumeSnapshot custom resource definition is available in the Kubernetes cluster.
Administrators can disable backup by setting the EmbeddedDatabaseBackupPlugin=false feature gate when installing the NuoDBaaS operator.
The table below lists backup configuration options for the DBaaS operator.
| Option | Description | Default value |
|---|---|---|
--database-backup-check-period | The period for checking database backup progress for not completed backups | 10s |
--backup-metadata-namespace | The namespace where the backup metadata is stored by the embedded backup plugin | DBaaS system namespace (if configured) or the default namespace |
--backup-volumesnapshot-class | The VolumeSnapshotClass name used for all VolumeSnapshot resources created by embedded backup plugin | Empty string ("") which indicate the default VolumeSnapshotClass |
--backup-post-hooks-on-snapshot-ready | Execute the post-backup hooks after the VolumeSnapshot resources are reported ready | false |
--backup-max-retry-count | The maximum number of retries performed by the embedded backup manager during backup execution | 4 |